A continuing debate centers on whether technology is the panacea that will help many students learn at higher levels or an exciting fad that is a temporary distraction from the real process of learning. The potential is there for either outcome. The degree to which technology has positive impacts on learning, depends on the way it is applied in the classroom and beyond. Implementation decisions and staff development will determine the positive or negative impact of technology.
The degree to which technology is beneficial to learning depends on the way it is applied in the classroom and beyond. When used effectively, technology offers great possibilities for expanding learning beyond what schools have taught before. Technology puts vast amounts of knowledge at students’ fingertips. Databases on every subject imaginable are available for study in all curriculum areas. Encyclopedias and complete collections of literary works reside on compact disk. Telecommunication satellite links expand the walls of classrooms to encompass the world.
Technology offers students a chance to delve deeply into a topic. Greater accessibility to information gives students the opportunity to gather data easily and analyze and synthesize that data in new ways. Students can manipulate data to identify the portions that are relevant to their needs. They can use data from one subject area in another area and integrate the information to enhance their understanding, giving them greater control over their learning.
Technology provides teachers with a tool to create their own teaching materials, to go beyond what is in the textbook and use alternate resources, and to organize information in new ways. Technology can be very helpful to teachers because it accommodates various learning styles and can enhance instructional strategies in many ways.
The way in which technology is used can be linked to  the quadrants of the Rigor/Relevance Framework. When used effectively, technology offers exciting possibilities for expanding learning beyond what schools have taught before.
the quadrants of the Rigor/Relevance Framework. When used effectively, technology offers exciting possibilities for expanding learning beyond what schools have taught before.
Technology links curriculum with real-world experiences both inside and outside the school. Using telecommunications and computer networks, students can work together in cooperative learning situations to help solve real problems, tying their education to real-life situations and giving them invaluable learning experiences. There are many ways that versatile powerful information technology can be used to enhance any of the instructional strategies. The chart lists a few ways that education technology can be used in each of the strategies.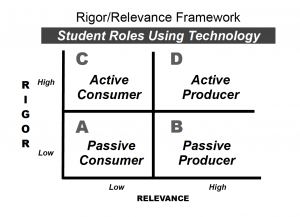
Quadrant A – In low rigor/low relevance instruction, the students is a passive consumer of technology, using information/communication tools to acquire new knowledge.
Quadrant B – In high relevance instruction, students become producers of student work creating routine web pages, spreadsheets and music learning to use technology effectively.
Quadrant C – In high rigor instruction, students become more active consumers using technology critically to do research or analyze data.
Quadrant D – In high rigor/high relevance, students are give challenges to create original work using technology whether is it composing music, creating art, constructing a robot or making new devices.
Technology is useful at all levels, but it important to relate the changing student role in using technical as teachers elevate rigor and relevance.
 hope this will give you a chance to experience another style of writing and publishing that uses technology effectively.
hope this will give you a chance to experience another style of writing and publishing that uses technology effectively.